Amazon EC2 G5 vs G6: Which GPU Instance is Worth Your Money?
Amazon’s EC2 instances are super flexible and have a wide range. When it comes to GPU compute, they have even more options. G5 and G6 are the latest two, each with a lot on paper but different GPUs and pricing. These aren’t just upgrades but different approaches to solving GPU-hungry workloads. G5 has been a workhorse for a while but G6 is supposed to be leaner, faster, and possibly more cost-effective. Are those promises worth the jump though? Let’s break down what each instance brings to the table, the GPUs involved and see how the pricing plays out.
Affiliate Disclosure
We are committed to being transparent with our audience. When you purchase via our affiliate links, we may receive a commission at no extra cost to you. These commissions support our ability to deliver independent and high-quality content. We only endorse products and services that we have personally used or carefully researched, ensuring they provide real value to our readers.
Table of Contents
AWS EC2 G5 vs G6: What is the difference?
The key difference between AWS EC2 G5 and G6 instances is the GPU: G5 uses the NVIDIA A10G, ideal for graphics-heavy tasks and moderately complex ML models, while G6 leverages the next-gen NVIDIA L4, optimized for deep learning inference and advanced video processing. G5 instances are generally cheaper compared to G6.
CUDO Compute offers a wide selection of high-performance NVIDIA and AMD GPUs to meet any AI or ML needs. Sign up now!
For a deeper understanding of CUDO Compute, take a look at this informative video:
Amazon EC2 G5 vs G6: In-depth Comparison
Both instances pack a punch, but they’re optimized for different workloads, pricing, and performance needs. So, how do you choose between them? Let’s look at the architecture, GPU models, storage, networking, and pricing—so by the end, you’ll know exactly which one suits your needs.
Let’s get into it.
The GPUs: NVIDIA A10G (G5) vs. NVIDIA L4 (G6)
The biggest difference between the G5 and G6 instances lies in the GPUs they offer. GPUs are the lifeblood of these instances, so knowing what each model brings to the table will help you make a smart choice.
NVIDIA A10G on G5 Instances
The G5 instances feature the NVIDIA A10G Tensor Core GPU, which is known for its strength in graphics-heavy applications and machine learning (ML) inference. This GPU is ideal for users who need to run remote workstations, video rendering, and gaming applications.
Key Specs of NVIDIA A10G:
- GPU Memory: 24 GB per GPU
- Tensor Cores: 320 third-generation NVIDIA Tensor Cores
- Performance: Up to 250 TOPS (Tera Operations Per Second)
- Ray Tracing Cores: 80 per GPU, ideal for realistic scene rendering
This combination of Tensor Cores and ray tracing power makes the A10G especially good for real-time, high-fidelity graphics. If you’re into video rendering, architectural visualization, or even game development, the G5 instance with A10G is designed to handle those tasks without breaking a sweat.
On the ML side, the A10G delivers solid performance for tasks like natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision. It’s cost-effective for training moderately complex ML models, especially when compared to older P3 instances.
NVIDIA L4 on G6 Instances
The G6 instances, on the other hand, come equipped with the NVIDIA L4 Tensor Core GPU, a next-gen chip optimized for deep learning inference and graphics-intensive workloads.
Key Specs of NVIDIA L4:
- GPU Memory: 24 GB per GPU
- Tensor Cores: Fourth-generation NVIDIA Tensor Cores
- Performance: Enhanced performance for deep learning inference
- RT Cores: Third-generation Ray Tracing Cores with DLSS 3.0 technology
The L4 GPU in G6 instances doubles the performance for deep learning inference compared to G4dn instances. This makes it a great choice for applications like language translation, speech recognition, and personalization algorithms. It also shines in real-time graphics tasks, supporting cinematic-quality rendering and game streaming.
The L4’s added AV1 hardware-encoding capabilities mean that it’s built for higher efficiency when handling video workloads, making it a strong contender for video analysis or AI-powered video content creation.
CUDO Compute lets you deploy top-tier GPUs like the H100, A100, and RTX A6000, all at unbeatable prices. Sign up now!
CPU and Architecture
When it comes to the underlying CPU architecture, both the Amazon EC2 G5 and G6 instances are powered by AMD EPYC processors. However, there are significant differences in the generation and performance characteristics of these processors, which directly impact how these instances perform for various tasks like graphics rendering, machine learning (ML) inference, and deep learning workloads.
G5 Instance: Second-Generation AMD EPYC Processors
G5 instances are using second Gen AMD EPYC processors which are known for their balance of performance and efficiency. These processors with the NVIDIA A10G GPUs make for a great combination of many graphics and ML workloads.
One of the big features of G5 instances is scalability. They can be configured up to 192 vCPUs which makes them suitable for more demanding workloads like multi-threaded applications like rendering, real-time graphics processing, and moderately complex machine learning training tasks.
Also, G5 instances support up to 100 Gbps of network bandwidth which is great for applications that require large datasets or when you need to train models that involve big data pipelines. Second Gen EPYC processors may not be the latest architecture but they offer a solid performance for customers who want to balance cost with capability, especially for graphics-heavy applications and ML inference tasks that don’t need the latest hardware.
G6 Instance: Third-Generation AMD EPYC Processors
G6 instances are a step up in terms of CPU architecture. They are using third-party AMD EPYC processors which brings improvements in compute power, memory bandwidth, and overall efficiency. The architecture improvements in these processors make G6 instances better suited for workloads that require high compute power like deep learning inference, complex NLP, and real-time video rendering.
While G6 also scales up to 192 vCPUs like G5, the performance gains from the third-gen EPYC processors make these instances more efficient for certain high-demand workloads. The newer CPU architecture means better power efficiency and faster data handling which makes G6 instances the better choice for customers with more compute-heavy applications. Also, G6 instances have the same up to 100 Gbps network bandwidth so they are well equipped to handle big workloads that require fast data throughput.
G6 has an edge over G5 since it uses third-gen EPYC processors. Especially for complex and high-demand workloads in deep learning and HPC.
For AI, rendering, or content creation, CUDO Compute provides cost-effective GPU resources without compromising on performance. Sign up now!
Storage and Network Bandwidth
When comparing Amazon EC2 G5 and G6 instances storage and network bandwidth are key, especially if you’re working with large datasets, high-performance workloads, or need fast data access and transfer speeds. These matter for machine learning (ML) training, high-end graphics rendering, or any application that involves real-time data processing. Let’s get into the details of storage and networking.
Storage Comparison
Storage is often forgotten but it’s a key part of high-performance computing, especially in fields like machine learning, video rendering, and data analysis. Both G5 and G6 instances have local NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSD storage which is known for its high read/write speeds and low latency. NVMe SSDs are a game changer for large datasets and high throughput workloads, they provide fast access to data which helps to avoid bottlenecks that can slow down your overall application performance.
G5 Instance: Up to 7.6 TB of Local NVMe SSD Storage
G5 instances have up to 7.6 TB of local NVMe SSD storage which is plenty of space for applications like training ML models, working with large datasets, and rendering complex video files. NVMe storage allows data to be accessed and processed faster than traditional SSDs which is important when you’re dealing with large amounts of data. For example, if you’re working with video rendering or gaming applications that require high data throughput NVMe storage ensures there are no bottlenecks in accessing data quickly.
The local storage in G5 instances is most beneficial for use cases where speed and performance matter like graphics-intensive applications or machine learning inference tasks. In those cases, NVMe storage provides fast data loading, quick read/write operations, and low latency so you can work with large datasets or render videos in real-time.
G6 Instance: Up to 7.52 TB of Local NVMe SSD Storage
G6 instances also have local NVMe SSD storage with up to 7.52 TB of storage. The storage capacity is almost the same as G5 instances and the benefits are the same. NVMe SSDs in G6 instances provide the same fast access to large datasets, high-speed read/write, and low latency.
Where G6 stands out is in its compute and memory efficiency with its 3rd gen AMD EPYC processors which complements the NVMe SSD storage. This makes G6 instances perfect for deep learning inference and other compute-intensive applications where both processing power and storage access speed need to be memory-optimized for peak CPU performance.
The storage capacity and type (NVMe SSD) in both G5 and G6 instances are the same. Both have fast local storage for demanding workloads. Whether you’re running high-performance ML models, batch processing, video processing applications, or gaming environments the local NVMe SSD storage in both instances ensures you have the speed and capacity to handle large amounts of data without slowdowns.
CUDO Compute offers easy-to-launch GPU instances and expert support to ensure you have everything you need to succeed. Sign up now!
Networking
Networking performance is important for workloads that require high-speed data transfer, especially in distributed computing development environments, real-time applications, or when working with large datasets. Both G5 and G6 instances have improved network throughput and low latency so it’s suitable for many applications.
G5 and G6 Instances: Up to 100 Gbps of Networking Bandwidth
Both G5 and G6 instances have up to 100 Gbps of networking which is more than enough for most high-performance workloads including ML training and inference, game streaming, and video processing. This high bandwidth allows for fast data transfer between nodes so you can process large datasets in-memory databases in real time. If you’re running applications like live video streaming, game development, or large-scale ML inference this level of network bandwidth ensures you won’t run into latency issues or data transfer bottlenecks.
The 100 Gbps bandwidth is useful in distributed machine-learning environments where multiple instances need to communicate with each other to train models across large datasets. It’s also important in gaming and video rendering applications where the real-time performance of web servers matters.
AWS Nitro System: Offloading Networking and Storage Tasks
Both G5 and G6 instances use the AWS Nitro System which is a specialized system that offloads networking, storage, and other virtualization tasks to dedicated hardware. The AWS Nitro System reduces the virtualization overhead typically associated with running virtual machines which results to better overall instance performance. With Nitro, storage and network I/O (Input/Output) are offloaded to separate components so the CPU and GPU can focus on processing workloads.
The result is better application performance, especially for workloads that require high-speed networking and fast data access like machine learning, video rendering, and gaming. By offloading the burden of networking and storage operations from the CPU the Nitro System ensures that both G5 and G6 instances perform at their best even when running demanding workloads.
Elastic Block Store (EBS) Bandwidth: G6 Has a Slight Edge
Both G5 and G6 instances have the same network bandwidth but G6 has slightly better Elastic Block Store (EBS) bandwidth than G5. This is important if you heavily rely on EBS for persistent data storage as better EBS performance means faster data access from external volumes.
EBS is useful when data needs to be persisted across instance reboots or terminations. If your workload involves large persistent datasets like data analytics, scientific cluster computing, or large-scale ML training the better EBS bandwidth in G6 instances can give you better performance and faster data access.
Access industry-leading GPUs like the H200 and L40S for deep learning and high-performance computing on CUDO Compute. Sign up now!
Use Cases:
Now that we’ve covered the technical specs, let’s break it down by use cases. Both G5 and G6 instances have their strengths, but they shine in different areas.
G5 Instance Use Cases
- Graphics-Intensive Applications: If you need high-end video rendering, 3D simulations, or virtual workstations, the G5 is your best bet. Its A10G GPU, with ray tracing cores and high memory bandwidth, can handle these tasks easily.
- Moderately Complex ML Training: If you’re working on tasks like NLP, computer vision, or recommendation systems, G5 provides a cost-effective solution for training these deep learning models. It’s not as powerful as the EC2 P4d instances, but it offers excellent price performance.
- Gaming and Virtual Reality: G5’s real-time rendering capabilities make it ideal for game development, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) applications. Its ability to create high-fidelity graphics quickly means you can develop immersive experiences without major delays.
G6 Instance Use Cases
- Deep Learning Inference: G6 instances with NVIDIA L4 GPUs are optimized for deep learning inference, which makes them a great choice if your workload is heavy on tasks like speech recognition, language translation, or image analysis.
- Graphics Workloads with Higher Memory Needs: The G6’s vCPU to RAM ratio of 1:8 makes it a solid choice for graphics-heavy workloads that require more memory. For example, complex video processing or high-definition game streaming can benefit from G6’s setup.
- AI-Driven Video Processing: If you’re handling large-scale video files for AI-based analysis or content generation, the L4 GPU’s AV1 hardware video encoding will give you an edge in efficiency.
Pricing: EC2 G5 vs G6
Pricing is always a major factor, especially when you’re deploying GPU instances for long-term or large-scale workloads. AWS offers different pricing models, including on-demand, reserved, and spot instances, so let’s break down the pricing for G5 and G6 based on on-demand rates.
G5 Instance Pricing
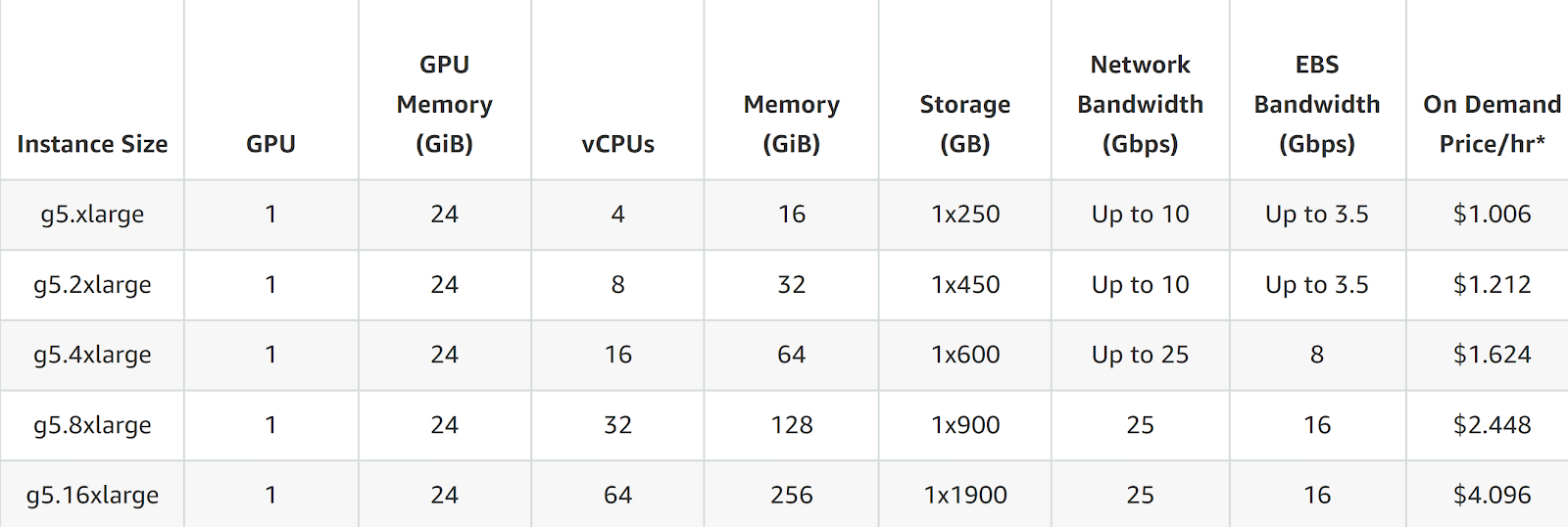
- g5.xlarge (1 GPU): $1.006 per hour
- g5.12xlarge (4 GPUs): $5.672 per hour
- g5.48xlarge (8 GPUs): $16.288 per hour
G6 Instance Pricing
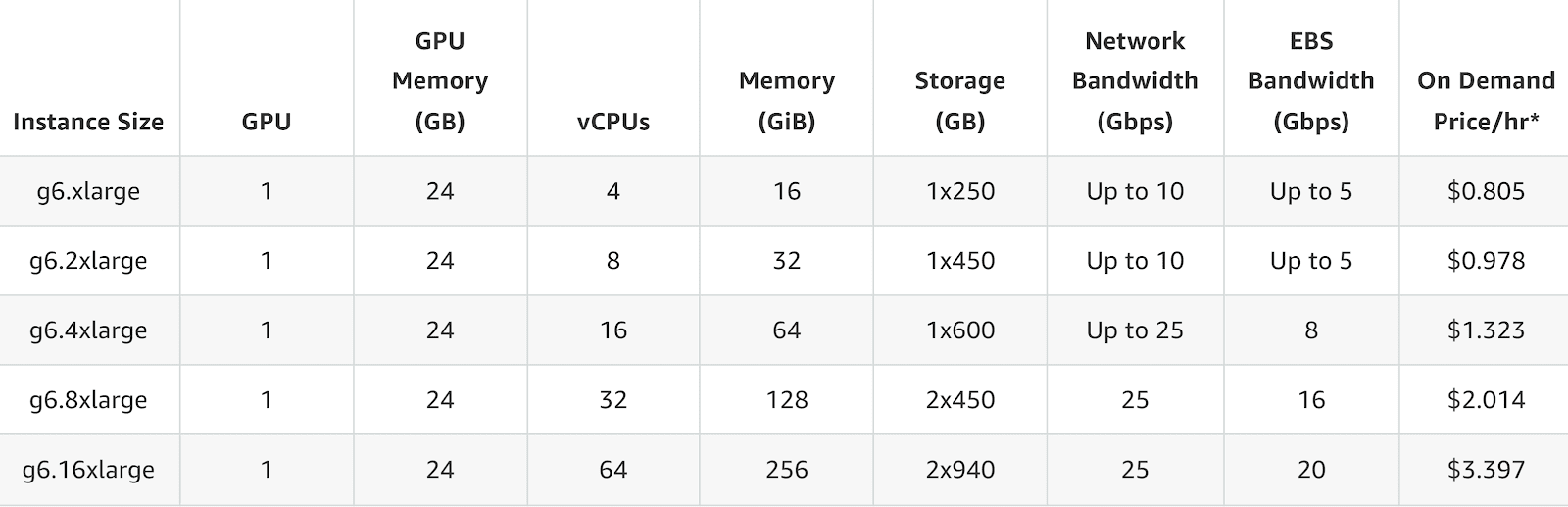
- g6.xlarge (1 GPU): $0.805 per hour
- g6.12xlarge (4 GPUs): $4.602 per hour
- g6.48xlarge (8 GPUs): $13.35 per hour
As you can see, G6 instances are generally cheaper than G5, especially for the larger burstable performance instances with multiple GPUs. This makes G6 a more cost-effective option if you’re running deep learning inference workloads or need high-performance graphics at scale.
Easily rent cloud GPUs on CUDO Compute and save significantly with competitive pricing on long-term plans. Sign up now!
Amazon EC2 G5 vs G6: The Bottom Line
So, which one is better—G5 or G6 instance type? The answer depends on your specific workload.
- Go with G5 if: You need high performance for graphics-heavy applications, remote workstations, or moderately complex ML training. The NVIDIA A10G GPU excels at real-time rendering, gaming, and simulations.
- Go with G6 if: Your focus is on deep learning inference, real-time video processing, or AI-driven video analysis. The NVIDIA L4 GPU is compute-optimized for these tasks, and you’ll also get better pricing for large-scale inference workloads.
At the end of the day, both G5 and G6 instances offer impressive performance, but understanding the specifics of your workload will help you choose the right instance for the job.
That’s a wrap! Hopefully, this breakdown gives you a clear understanding of how the EC2 G5 and G6 instances stack up against each other. Whatever your workload demands—be it ML, graphics, or video processing—AWS has you covered with these powerful GPU-based instances.
Get started today on CUDO Compute and build the perfect GPU cloud with the right balance of cost and performance. Sign up now!